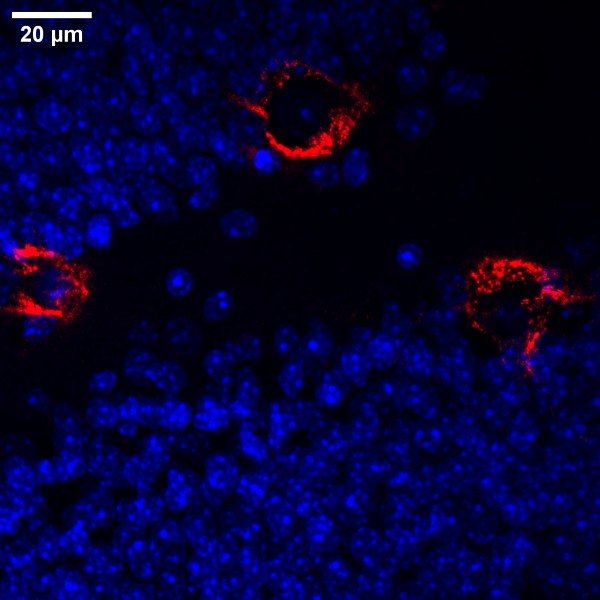
Human olfactory mucosa cell model opens a new perspective on Alzheimer’s disease: Researchers at the University of Eastern Finland have developed and characterized a new cell model for Alzheimer’s disease that has wide utility for research and could prove useful in early diagnosis and testing of new therapies. In collaboration with clinicians at Kuopio University […]
Read More… from Human olfactory mucosa cell model opens a new perspective on Alzheimer’s disease